Computability Part 6: Von Neumann Architecture
During the previous posts, we covered Turing machines, tag systems, and cellular automata. All of these are equivalent in terms of what they can compute, but some are more practical than others. In this post, we'll look at the von Neumann architecture of physical computers and implement an extremely inefficient machine, write a few programs targeting it, then prove it is Turing complete.
John von Neumann was a famous mathematician and physicist. Contemporary with Alan Turing, he was aware of Turing's work on Turing machines and computability. At the same time, von Neumann was involved in the Manhattan Project which required lots of computation provided by some early computers. Thus he got involved in computer design. Unlike a Turing machine, a physical computer can't have an infinite tape and while data is processed based on input and states, this needs to be more ergonomic than Yurii Rogozhin's 4-state 6-symbol machine we described in Part 2.
Von Neumann described a computer architecture as consisting of the following components1:
- A central arithmetic component (CA) handling calculation.
- A central control component (CC) driving which calculations should be performed.
- Memory (M) for storage.
- Input (I) and output (O) components to get data into the system and to communicate results outside of the system, from/to a recording medium (R)
Here is a diagram of this architecture:
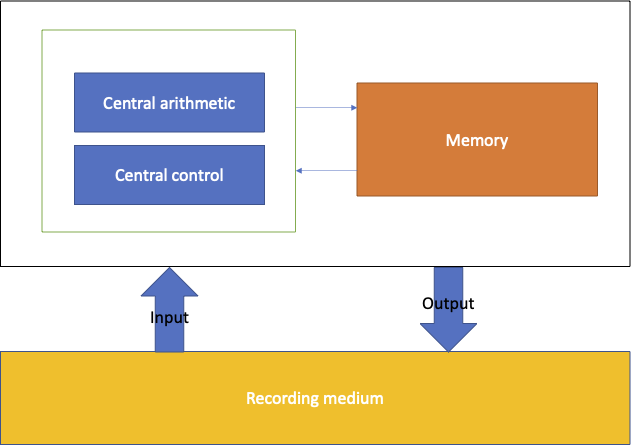
Before von Neumann, computers were single-purpose devices - the programming was hardwired. One of the major innovations, which might not be apparent, is the introduction of a central control component and the ability of the memory to store not only data but also the program itself. This makes devices based on this architecture able to be reprogrammed to perform different tasks.
We can now load an arbitrary program into memory. The program will use the instructions which our central arithmetic understands to perform computations. The central control can read this program and have the central arithmetic perform the required operations. During execution, data is also read from/written to memory.
Programs (and data) is loaded into memory through the input component and results are sent through the output component.
While over the following decades this architecture got tweaked and tuned, it's pretty obvious it is the ancestor of all modern computers: computers still have CPUs, which include control and arithmetic, and memory.
Let's create a virtual machine based on this architecture.
Implementation
We will create a very simple machine based on this architecture in Python. In subsequent posts, we will look at other designs, but we're starting with a direct translation of this architecture.
Input
The interface to our input component is a function that, when called, returns an integer. This is all our machine needs to get data.
We will implement this over a text file. Our input component will buffer
this file into a list and expose a read_one() function that will
return one integer (as returned by [ord()]{.title-ref}) for each
character from the buffer.
def inp(file):
buffer = list(open(file).read())
return lambda: ord(buffer.pop(0))
Output
The interface to our output component is a function that takes an integer as an argument. This is all our machine needs to output one memory cell.
We will implement this using print() and actually convert the given
integer to a character. This is just to provide a convenient way for us
to look at output like Hello world!
.
def out(value):
print(chr(value), end='')
Memory
Our memory will consist of a list of 10000 integers. We will zero-initialize the list, then load a program from a file to memory, starting at address 0. We expect the program to consist of a series of integers separated by a space or a newline character. We'll use this encoding to make it easier for us to peek at the code targeting our von Neumann machine.
def memory(file):
memory = [0] * 10000
for i, value in enumerate(' '.join(open(file).readlines()).split()):
memory[i] = int(value)
10000 is chosen arbitrarily, at this point we're not worrying about word size, page alignment etc. We simply have room to store 10000 integers in our memory, which will include both code and data.
CPU
We'll package the control and arithmetic components into a CPU class.
We'll initialize this class with memory, input, and output components.
class CPU:
def __init__(self, memory, inp, out):
self.memory, self.inp, self.out = memory, inp, out
Central control
Our control unit will maintain a program counter (PC), an index into
the memory pointing to the next instruction to execute. The machine runs
by reading 3 integers from memory (at PC, PC + 1 and PC + 2), and
passing these to the arithmetic unit for processing. The program counter
is then incremented by 3. This repeats until PC goes outside the
bounds of the memory, at which point the machine halts (alternately we
could have provided some HALT instruction).
def run(self):
self.pc = 0
while self.pc < len(self.memory):
instr, m1, m2 = self.memory[self.pc:self.pc + 3]
self.process(instr, m1, m2)
self.pc += 3
We will implement process() next.
Central arithmetic
Our arithmetic unit will process triples of
<Instruction> <memory address 1> <memory address 2>. It will support 8
instructions:
ATwill set the value atmemory address 1to be the value at the memory address specified by the value atmemory address 2(in short,m[m1] = m[m[m2]]).SETwill set the value at the memory address specified by the value atmemory address 1to be the value atmemory address 2(in short,m[m[m1]] = m[2]).ADDwill update the value atmemory address 1by adding the value atmemory address 2to it (in short,m[m1] += m[m2]).NOTwill update the value atmemory address 1to be 0 if the value atmemory address 2is different than 0, or 1 if the value atmemory address 2is 0 (in short,m[m1] = !m[m2]).EQwill compare the values atmemory address 1andmemory address 2and update the value atmemory address 1to be 1 if they are equal, 0 otherwise (in short,m[m1] = m[m1] == [m2]).JZwill perform a conditional jump - if the value atmemory address 1is 0, it will update the program counter to point tomemory address 2(in short,if !m[m1] then PC = m[m2]).INPwill read one integer from the input and store it atmemory address 1+ an offset value specified atmemory address 2(in short,m[m1 + m[m2]] = inp()).OUTwill write the value atmemory address 1+ an offset value specified atmemory address 2to the output (in short,out(m[m1 + m[m2]]).
Since the instructions are also read from memory, which is a list of
integers, we will encode them as integers: AT = 0, SET = 1, ...
OUT = 7.
def process(self, instr, m1, m2):
match instr:
case 0: # AT
self.memory[m1] = self.memory[self.memory[m2]]
case 1: # SET
self.memory[self.memory[m1]] = self.memory[m2]
case 2: # ADD
self.memory[m1] += self.memory[m2]
case 3: # NOT
self.memory[m1] = +(not self.memory[m2])
case 4: # EQ
self.memory[m1] = +(self.memory[m1] == self.memory[m2])
case 5: # JZ
if not self.memory[m1]:
# Set PC to m2 - 3 since run() will increment PC by 3
self.pc = m2 - 3
case 6: # INP
self.memory[m1 + self.memory[m2]] = self.inp()
case 7: # OUT
out(self.memory[m1 + self.memory[m2]])
case _:
raise Exception("Unknown instruction")
Von Neumann VM
Putting it all together, we'll take two input arguments: the first one
(argv[1]) will represent the code input file containing the program,
the second one (argv[2]) will be the file containing additional input
to be consumed by the inp() function:
import sys
vn = CPU(memory(sys.argv[1]), inp(sys.argv[2]), out)
vn.run()
Here is our von Neumann virtual machine in one listing:
def inp(file):
buffer = list(open(file).read())
return lambda: ord(buffer.pop(0))
def out(value):
print(chr(value), end='')
def memory(file):
memory = [0] * 10000
for i, value in enumerate(' '.join(open(file).readlines()).split()):
memory[i] = int(value)
return memory
class CPU:
def __init__(self, memory, inp, out):
self.memory, self.inp, self.out = memory, inp, out
def run(self):
self.pc = 0
while self.pc < len(self.memory):
instr, m1, m2 = self.memory[self.pc:self.pc + 3]
self.process(instr, m1, m2)
self.pc += 3
def process(self, instr, m1, m2):
match instr:
case 0: # AT
self.memory[m1] = self.memory[self.memory[m2]]
case 1: # SET
self.memory[self.memory[m1]] = self.memory[m2]
case 2: # ADD
self.memory[m1] += self.memory[m2]
case 3: # NOT
self.memory[m1] = +(not self.memory[m2])
case 4: # EQ
self.memory[m1] = +(self.memory[m1] == self.memory[m2])
case 5: # JZ
if not self.memory[m1]:
# Set PC to m2 - 3 since run() will increment PC by 3
self.pc = m2 - 3
case 6: # INP
self.memory[m1 + self.memory[m2]] = self.inp()
case 7: # OUT
out(self.memory[m1 + self.memory[m2]])
case _:
raise Exception("Unknown instruction")
import sys
vn = CPU(memory(sys.argv[1]), inp(sys.argv[2]), out)
vn.run()
We can save this as vn.py.
Let's create a Hello world!
program targeting this machine. We will
use the OUT instruction to output each character of Hello
and a
new line (\n). We'll first tell the VM to output the values at memory
address 21 to 26:
7 21 9999
7 22 9999
7 23 9999
7 24 9999
7 25 9999
7 26 9999
We are referencing addresses 21 to 26 plus the offset 0 (the value at
memory 9999, since our memory is initialized with zeros).
We want to halt after this, so we need to jump our program counter to
10000. We will do this by using our JZ instruction, saying if the
memory value at index 9999 is 0, jump to 10000:
5 9999 10000
Now we get to memory address 21, so we will set the values of memory 21
to 26 to the values of the characters in Hello
(as returned by
ord()) plus a 10 for \n:
72 101 108 108 111 10
Here is the full listing which we can save as hello.vn:
7 21 9999
7 22 9999
7 23 9999
7 24 9999
7 25 9999
7 26 9999
5 9999 10000
72 101 108 108 111 10
We can then use our VM to run the program like this:
touch input
python3 vn.py hello.vn input
We're also creating a blank input file since Hello world!
isn't
going to read anything via inp().
Running this should print Hello. Our program
is pretty hard to
write or read, we're programming with integers. Let's make our life a
bit easier.
Assembler
We will implement an assembler for our VM. An assembly language is a low-level language closely matching the architecture it targets (in our case, our very simple von Neumann machine).
Our assembler will take 2 arguments - an input file and an output file - and automatically translate the input (assembly language) into instructions for our VM.
We will add the following features:
- Comments - Lines starting with
#will be ignored. - Instructions - We will express our instructions as
at,set,add,not,eq,jz,inp,outto represent the instructions0,1, ...5. - Labels - We will tag a location in the code by a string ending in
:, for exampleHERE:. We will then be able to refer to the location using the identified preceded by:, like:HERE. We will also allow adding an offset to a reference::HERE+2is 2 past theHERElabel. ORDmacro - To make implementingHello world!
easier, we will provide theORD()macro which will return the integer representation of the character passed to it, for exampleORD(H)will return72.
Using this assembly language, we can rewrite Hello world!
as:
## Print 6 characters starting from DATA
out :DATA 9999
out :DATA+1 9999
out :DATA+2 9999
out :DATA+3 9999
out :DATA+4 9999
out :DATA+5 9999
## End program
jz 9999 10000
## Data section
DATA: ORD(H) ORD(e) ORD(l) ORD(l) ORD(o) 10
First, we'll read the input file and convert it into a list of tokens.
We will ignore lines starting with # (so we can add comments to our
assembly file).
import sys
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print("Usage: asm.py <input> <output>")
exit()
## Read all lines into a list
lines = open(sys.argv[1]).readlines()
## Filter out blank lines and lines starting with '#'
lines = list(filter(lambda line: line and line[0] != '#', lines))
## Join all lines and split into tokens
tokens = ' '.join(lines).split()
The labels themselves aren't part of the program, rather mark locations in the program, so in the next step we will pluck these out from the list of tokens but retain the index they are referencing:
## pluck labels and remember position
labels, i = {}, 0
while i < len(tokens):
# If not a label, advance
if tokens[i][-1] != ':':
i += 1
continue
# Store location and pluck label
labels[tokens[i][:-1]] = i
tokens.pop(i)
Now we will process all tokens and handle the following cases:
- If token starts with
:, it is a label reference, so replace it with the actual location (as stored during the previous step). - If the token is an op code, replace it with the integer value of the op code.
- If the token is an
ORD()macro, replace the character passed toORD()with its value.
## Op code list (constant)
OP_CODES = ['at', 'set', 'add', 'not', 'eq', 'jz', 'inp', 'out']
for i, token in enumerate(tokens):
# replace label references with actual position
if token[0] == ':':
if '+' in token:
base, offset = token.split('+')
tokens[i] = labels[base[1:]] + int(offset)
else:
tokens[i] = labels[token[1:]]
# replace op codes with values
if token in OP_CODES:
tokens[i] = OP_CODES.index(token)
# replace ORD macro
if token[:4] == 'ORD(':
tokens[i] = ord(token[4:-1])
Finally, we write all tokens to the output file:
open(sys.argv[2], "w").write(
' '.join([str(token) for token in tokens]))
Here is the full source code of our assembler (asm.py):
import sys
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print("Usage: asm.py <input> <output>")
exit()
## Read all lines into a list
lines = open(sys.argv[1]).readlines()
## Filter out blank lines and lines starting with '#'
lines = list(filter(lambda line: line and line[0] != '#', lines))
## Join all lines and split into tokens
tokens = ' '.join(lines).split()
## pluck labels and remember position
labels, i = {}, 0
while i < len(tokens):
# If not a label, advance
if tokens[i][-1] != ':':
i += 1
continue
# Store location and pluck label
labels[tokens[i][:-1]] = i
tokens.pop(i)
## Op code list (constant)
OP_CODES = ['at', 'set', 'add', 'not', 'eq', 'jz', 'inp', 'out']
for i, token in enumerate(tokens):
# replace label references with actual position
if token[0] == ':':
if '+' in token:
base, offset = token.split('+')
tokens[i] = labels[base[1:]] + int(offset)
else:
tokens[i] = labels[token[1:]]
# replace op codes with values
if token in OP_CODES:
tokens[i] = OP_CODES.index(token)
# replace ORD macro
if token[:4] == 'ORD(':
tokens[i] = ord(token[4:-1])
open(sys.argv[2], "w").write(
' '.join([str(token) for token in tokens]))
We can now save our assembly Hello world!
(listed above) to a file,
let's call it hello.asm and use the assembler to convert it to a
program our VM can execute:
python3 asm.py hello.asm hello.vn
The resulting hello.vn should have the same content as our
hand-crafted Hello world!
, minus the newlines (the assembler
doesn't output newlines). The content of the assembled file hello.vn
is:
7 21 9999 7 22 9999 7 23 9999 7 24 9999 7 25 9999 7 26 9999 5 9999 10000 72 101 108 108 111 10
We can run this using:
python3 vn.py hello.vn input
We are again using an empty input file since we don't need input. As a
convention, we use the .asm extensions for assembly files and .vn
for assembled files targeting the VM.
Variables and loops
Let's rewrite our program: instead of outputting :DATA, then
:DATA+1, then DATA+2... we should be able to output :DATA + :I
where :I goes from 0 to 5.
We can easily use a variable by tagging any part of the program then referencing it, then using that label to refer to the variable.
I: 0
Then we can use :I to reference to it. We will use a COUNTER
variable to count down from 6 to 0, and an offset variable I:
## Variables
I: 0
COUNTER: 6
We also need a couple of constant values: 0, 1 - by which we
increment I during each iteration, and -1 to decrement COUNTER
during each iteration. And, of course, our DATA, where we store the
Hello
string:
## Constants
CONST: 0 1 -1
## Data
DATA: ORD(H) ORD(e) ORD(l) ORD(l) ORD(o) 10
Now lets look at how we can implement a loop using JZ:
## Beginning of loop
LOOP:
## Output I
out :DATA :I
## Decrement COUNTER, increment I
add :COUNTER :CONST+2
add :I :CONST+1
## If COUNTER is 0, we're done
jz :COUNTER 10000
## If not, jump to the start of the loop
jz :CONST :LOOP
At each iteration, our loop will output the character value at DATA
plus the offset specified in I (initially 0). Then we subtract -1 from
our COUNTER and add 1 to I. Since our VM uses memory addresses for
all operations, we stored 1 and -1 in memory at CONST and
CONST+1 respectively.
If COUNTER is 0, we're done, so we jump to 10000. If not, we repeat
the loop (jump to LOOP if CONST is 0, but CONST is always 0).
Here is the full listing of this program:
## Beginning of loop
LOOP:
## Output I
out :DATA :I
## Decrement COUNTER, increment I
add :COUNTER :CONST+2
add :I :CONST+1
## If COUNTER is 0, we're done
jz :COUNTER 10000
## If not, jump to the start of the loop
jz :CONST :LOOP
## Constants
CONST: 0 1 -1
## Data
DATA: ORD(H) ORD(e) ORD(l) ORD(l) ORD(o) 10
## Variables
I: 0
COUNTER: 6
We can save this as hello2.asm, then assemble and run it:
python3 asm.py hello2.asm hello2.vn
python3 vn.py hello2.vn
Notes
A few notes: data is mixed with code in all our programs, which follows from the von Neumann architecture, in which the memory of the system stores both code and data. This is fundamentally true for all computers, and enables some interesting behavior like self-modifying code. This could be intentional, or we could, accidentally due to a bug, interpret data as code or vice-versa, code as data. Modern systems employ various additional protections to prevent this type of accidental usage.
Because our particular VM starts execution from memory location 0, we have to place our constants and variables (data) after the instructions in the program. Executable files on modern systems similarly contain code and data segments, albeit with more complex layout and rules.
Turing-completeness
Let's prove our simple von Neumann VM is Turing-complete, meaning capable of universal computation. As we saw throughout this series of blog posts, the best way to prove this is to emulate another known Turing-complete system.
We will prove this by implementing a
Brainfuck interpreter. We
covered Brainfuck during the second post in the
series,
under Esoteric Turing machines. To recap: Brainfuck (BF) uses a byte
array (tape), a data pointer (index in the array), and 8 symbols: >,
<, +, -, ., ,, [, ]. The symbols are interpreted as:
>: Increment the data pointer (move head right).<: Decrement the data pointer (move head left).+: Increment array value at data pointer.-: Decrement array value at data pointer..: Output value at data pointer.,: Read 1 byte of input and store at data pointer.[: If the byte at data pointer is 0, jump right to the matching], else increment data pointer.]: If the byte at data pointer is not 0, jump left to the matching[, else decrement data pointer.
We will use our assembly language to implement a program which reads a BF program from input, then executes it. Effectively, we'll use our very simple virtual machine to emulate another very simple virtual machine!
I won't cover the details of the implementation, since it is quite cumbersome due to the simplicity of our VM and assembly language. I will just provide a short summary of what is going on:
- We'll start by reading the BF program from input, until we
encounter a newline (
\). - We will use a
CODE_PTRcode pointer variable to point to the current BF instructions and aDATA_PTRdata pointer variable to point to the BF array. - We'll overlay the BF array BF array over the VM memory, starting at address 5000 (middle of our memory).
- We will then handle each possible input (
>,<, etc.). - Most of the instructions are easy to implement, the most complex are
[and], which require keeping track of unbalanced parenthesis so we properly jump from[to matching]and vice-versa.
Here is the full Brainfuck interpreter implemented in our assembly language:
## Read Brainfuck program until a \n is encountered
START:
## Read one integer at PROG + offset I
inp :PROG :I
## Increment I by 1
add :I :CONST+1
## Zero out DONE_READING (!1)
not :DONE_READING :CONST+1
## DONE_READING = 10
add :DONE_READING :CONST+3
## Load the last integer we read in TEMP
at :TEMP :END
## Increment END to keep track of program end
add :END :CONST+1
## Check if the last integer we read was 10 (\n)
eq :DONE_READING :TEMP
## If it wasn't zero, jump to start and read another value
jz :DONE_READING :START
## Start running program
BF_RUN:
at :TEMP :CODE_PTR
add :CODE_PTR :CONST+1
## Check if we're on a > instruction
not :TEMP2 :CONST+1
add :TEMP2 :BF
eq :TEMP2 :TEMP
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
jz :TEMP2 :RIGHT
## Check if we're on a < instruction
not :TEMP2 :CONST+1
add :TEMP2 :BF+1
eq :TEMP2 :TEMP
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
jz :TEMP2 :LEFT
## Check if we're on a + instruction
not :TEMP2 :CONST+1
add :TEMP2 :BF+2
eq :TEMP2 :TEMP
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
jz :TEMP2 :INC
## Check if we're on a - instruction
not :TEMP2 :CONST+1
add :TEMP2 :BF+3
eq :TEMP2 :TEMP
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
jz :TEMP2 :DEC
## Check if we're on a . instruction
not :TEMP2 :CONST+1
add :TEMP2 :BF+4
eq :TEMP2 :TEMP
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
jz :TEMP2 :OUT
## Check if we're on a , instruction
not :TEMP2 :CONST+1
add :TEMP2 :BF+5
eq :TEMP2 :TEMP
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
jz :TEMP2 :IN
## Check if we're on a [ instruction
not :TEMP2 :CONST+1
add :TEMP2 :BF+6
eq :TEMP2 :TEMP
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
jz :TEMP2 :FORWARD
## Check if we're on a ] instruction
not :TEMP2 :CONST+1
add :TEMP2 :BF+7
eq :TEMP2 :TEMP
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
jz :TEMP2 :BACKWARD
## No matching BF instruction so we're done
jz :CONST 10000
RIGHT:
## > - increment data pointer
add :DATA_PTR :CONST+1
jz :CONST :BF_RUN
LEFT:
## < - decrement data pointer
add :DATA_PTR :CONST+2
jz :CONST :BF_RUN
INC:
## + - increment cell
at :TEMP :DATA_PTR
add :TEMP :CONST+1
set :DATA_PTR :TEMP
jz :CONST :BF_RUN
DEC:
## - - decrement cell
at :TEMP :DATA_PTR
add :TEMP :CONST+2
set :DATA_PTR :TEMP
jz :CONST :BF_RUN
OUT:
## . - output cell
at :TEMP :DATA_PTR
out :TEMP :CONST
jz :CONST :BF_RUN
IN:
## , - store input in cell
inp :TEMP :CONST
set :DATA_PTR :TEMP
jz :CONST :BF_RUN
FORWARD:
## [
at :TEMP :DATA_PTR
not :TEMP :TEMP
## If value in cell is not 0, continue
jz :TEMP :BF_RUN
## Find matching ]
## Set TEMP to 1, counting unbalanced [
not :TEMP :TEMP
add :TEMP :CONST+1
SCAN_FORWARD:
at :TEMP2 :CODE_PTR
eq :TEMP2 :BF+6
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
## Jump if found a [
jz :TEMP2 :FORWARD_LPAR
at :TEMP2 :CODE_PTR
eq :TEMP2 :BF+7
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
## Jump if found a ]
jz :TEMP2 :FORWARD_RPAR
## Keep scanning
add :CODE_PTR :CONST+1
jz :CONST :SCAN_FORWARD
## Increment counter when finding a [
FORWARD_LPAR:
add :TEMP :CONST+1
add :CODE_PTR :CONST+1
jz :CONST :SCAN_FORWARD
## Decrement counter when finding a ]
FORWARD_RPAR:
add :TEMP :CONST+2
## If counter is 0, we're done
jz :TEMP :BF_RUN
## Else keep scanning
add :CODE_PTR :CONST+1
jz :CONST :SCAN_FORWARD
BACKWARD:
## ]
at :TEMP :DATA_PTR
## If value in cell is 0, continue
jz :TEMP :BF_RUN
## Find matching [
## Set TEMP to 1, counting unbalanced ]
not :TEMP :TEMP
add :TEMP :CONST+1
## Move code pointer back 2
add :CODE_PTR :CONST+2
add :CODE_PTR :CONST+2
SCAN_BACKWARD:
at :TEMP2 :CODE_PTR
eq :TEMP2 :BF+6
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
## Jump if found a [
jz :TEMP2 :BACKWARD_LPAR
at :TEMP2 :CODE_PTR
eq :TEMP2 :BF+7
not :TEMP2 :TEMP2
## Jump if found a ]
jz :TEMP2 :BACKWARD_RPAR
## Keep scanning
add :CODE_PTR :CONST+2
jz :CONST :SCAN_BACKWARD
## Decrement counter when finding a [
BACKWARD_LPAR:
add :TEMP :CONST+2
## If counter is 0, we're done
jz :TEMP :BF_RUN
## Else keep scanning
add :CODE_PTR :CONST+2
jz :CONST :SCAN_BACKWARD
## Increment counter when finding a ]
BACKWARD_RPAR:
add :TEMP :CONST+1
add :CODE_PTR :CONST+2
jz :CONST :SCAN_BACKWARD
CONST: 0 1 -1 10
BF: ORD(>) ORD(<) ORD(+) ORD(-) ORD(.) ORD(,) ORD([) ORD(])
I: 0
TEMP: 0
TEMP2: 0
END: :PROG
DONE_READING: 0
CODE_PTR: :PROG
DATA_PTR: 5000
## We'll load the BF program here
PROG:
We can save this program as bf.asm. We will also create a Brainfuck
program to run - Hello world
:
++++++++[>++++[>++>+++>+++>+<<<<-]>+>+>->>+[<]<-]>>.>---.+++++++..+++.>>.<-.<.+++.------.--------.>>+.>++.
We will save this as hello.bf. Now we can compile our BF interpreter
and run it using our VM:
python3 asm.py bf.asm bf.vn
python3 vn.py bf.vn hello.bf
This should output Hello world!
.
Since Brainfuck is Turing-complete and our VM can emulate a Brainfuck interpreter, our VM is also Turing-complete.
Summary
- We talked about the von Neumann architecture and looked at a simple VM built using this architecture.
- We created an assembler targeting this VM, to make it easier to write code that runs on the VM.
- We looked at a couple of versions of
Hello world
, and saw how we can use variables and loops. - Finally, we implemented a Brainfuck interpreter that runs on the VM, proving our von Neumann machine is Turing-complete.
For convenience, the code we covered in this post is online here: